Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis
What is the thyroid?
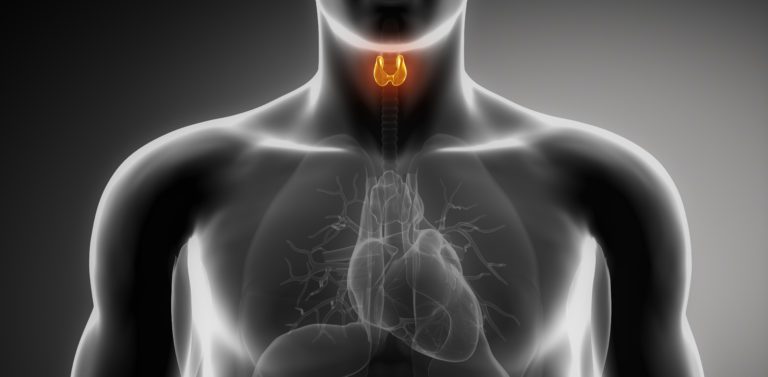
The thyroid gland is a small butterfly-shaped organ located at the base and center of the neck and it is a part of the endocrine system. The job of the thyroid gland is to make thyroid hormones which regulate widespread symptoms in the body such as body temperature, metabolic rate, digestive functions, brain functions, muscle, mental and cognitive functions. As you can see, it regulates functions related to every aspect of our lives; how we feel, what energy we are producing, how our body digest foods, and our interactions with others. When it becomes inflamed or swollen and has limited ability to produce hormones, this is known as thyroiditis.
When the thyroid cannot function properly, the entire body suffers. This type of thyroiditis is the most commonly occurring form of this autoimmune disease and involves severe inflammation of the thyroid gland. According to EndocrineWeb, Hashimoto’s hypothyroidism affects an estimated 14 million people in the United States. It is sometimes referred to as chronic lymphocytic thyroiditis and generally affects women, who have a risk of being diagnosed with this disease at a 7 to 1 ratio against men. Being that thyroiditis is an autoimmune disease, this means that the body is using its own defense mechanisms against itself and destroying healthy tissue in the thyroid gland. This hormone disruption is part of thyroiditis that can severely hinder a person’s life, being left restless, and tired during the day due to the lack of sleep and anxiety.
Symptoms of Hashimoto’s thyroiditis
People with this condition and are often unaware they are affected because of a lack of visible or physical symptoms, they attribute feeling off to other causes. Learning the symptoms is the first step of your solution. A person can go years with the symptoms without a proper diagnosis.
The most common symptoms are:
- Drowsiness
- Heavy and irregular menstrual cycles in women
- Trouble breathing as a result of the goiter
- Constipation
- Drying of the hair
- Skin and nails
- Increased cold sensitivity
- fatigue
- Weight gain
- Depression
- Irritability
- Puffy face
- anxiety
All of these arise when your body is unable to regulate its temperate and metabolism naturally.
Getting Diagnosed
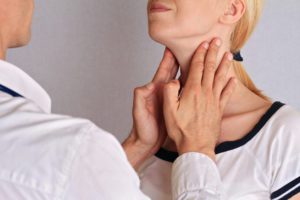
Getting diagnosed from Hashimoto’s hypothyroid is based on the symptoms you are experiencing and blood test that checks your hormone levels. Depending on how high or low your thyroid hormone levels are, your doctor can determine whether or not you’re suffering from a low thyroid production. The formal diagnosis of Hashimoto’s may take years to happen, you can be suffering from the symptoms and not have blood test show it.
Hashimoto’s thyroiditis is an autoimmune disease and as such, there will be antibodies focused on eliminating the enzyme thyroid peroxidase. By using a thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) test, it may detect and diagnose the disease before the symptoms become too advanced. The TSH test helps gauge the specific dosage needed for medicines and synthetic hormones.
Treatment Options: conventional medicine
The treatments for this type of autoimmune disease will vary and depend on what your body responds best to. Conventional medicine, meaning your doctor, will always suggest using synthetic (medicinal) hormones to replace those that are not produced. Using these medicines will allow your body to regulate its own hormones and repair your metabolic levels. Like other types of medicines, the pills come in a range of dosages and your doctor will help determine how strong or weak a prescription is needed for your symptoms. Besides these factors, any other medication or allergies will impact your treatment selections.
To ensure the best treatment, a thyroid-stimulating hormone test will be administered to see which route and dosages are working best. If the goiter caused by this disease grows too large and is not reducing even after medicinal treatment, it might be necessary to have surgery to remove the thyroid gland. Because the thyroid is producing less, it will be necessary to supplement the body with synthetic hormones. These hormones are made to mimic the naturally occurring hormones like thyroxine. The dosages might change over time but it’s very possible that once medication begins, it will be needed for the rest of your life.
There are some risks involved with using synthetic hormones and they arise from taking a higher dosage than necessary. Hormone replacement must be done slowly and closely monitored in order to give your heart and endocrine system time to adjust.
Natural ways of healing Hashimoto’s Disease
Treating Hashimoto’s disease is a lifelong process that includes making lifestyle and diet changes.
The first step is to remove foods that aid inflammation and the cause the symptoms. These are gluten and grain products with similar chemistry to gluten – corn, rice, beans, al dairy products, eggs, soy and sugary foods. Learn more about the Autoimmune Protocol Diet which is designed to heal from Autoimmune disease. The diet will supplement inflammatory foods with nutrient dense food. I may seem overwhelming to go without these foods that are staple to our diet, but, as you begin to feel better, you will not miss nor crave them. We are going to substitute these foods with nourishing choices.
Second step is to increase supplements in your body that are not allowing the thyroid hormone to be produced at normal levels.
These supplements include:
- Iodine
- Zinc
- Selenium
- Vitamin D
- B12 and iron
- Ashwagandha
- L-Tyrosine
Third step is to implement a probiotic supplement into your daily routine. This will help with digestion and for the gut to detox properly. Think of it as aiding your gut get rid of toxins.
The last step in treating Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis is managing stress. Daily exercise helps reduce stress by flushing negative emotions and substituting with positive emotions. Be open to try different exercise options to manage your stress, there are so many different types that work well like walking, running, cycling, kickboxing, yoga and all can be combined with daily meditation for your brain.
Key Takeaways
- Hashimoto’s thyroiditis is a common and widespread autoimmune disease that affects many people across the globe. The symptoms might appear to be other medical conditions so diagnosing it can be difficult.
- As an autoimmune disease, the immune system is attacking the cells it finds as foreign, in this case, the thyroid. There are various treatment options including medicine which does not cure the problem but merely puts a bandage on the symptoms or natural ways to fight through lifestyle options and AIP diet.
- Detox from all the metals and toxins that are causing inflammation is an important part of treatment, this includes not eating inflammatory foods and taking a daily probiotic to have the digestive system flowing nicely.







Leave a Reply